Notes
two squares ii solution
Solution to the Two Squares II Puzzle
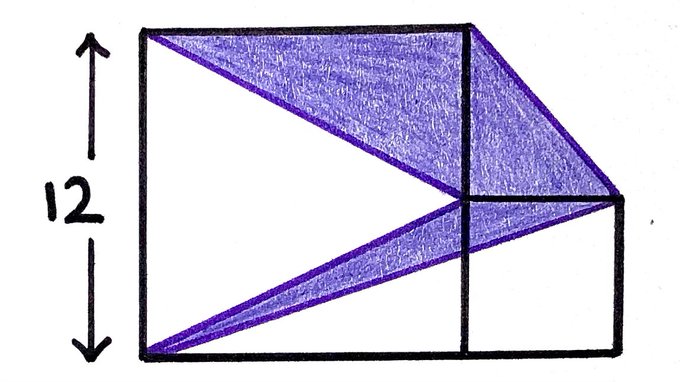
Two squares. What’s the shaded area?
Solution by Area of a Triangle and Area of a Trapezium
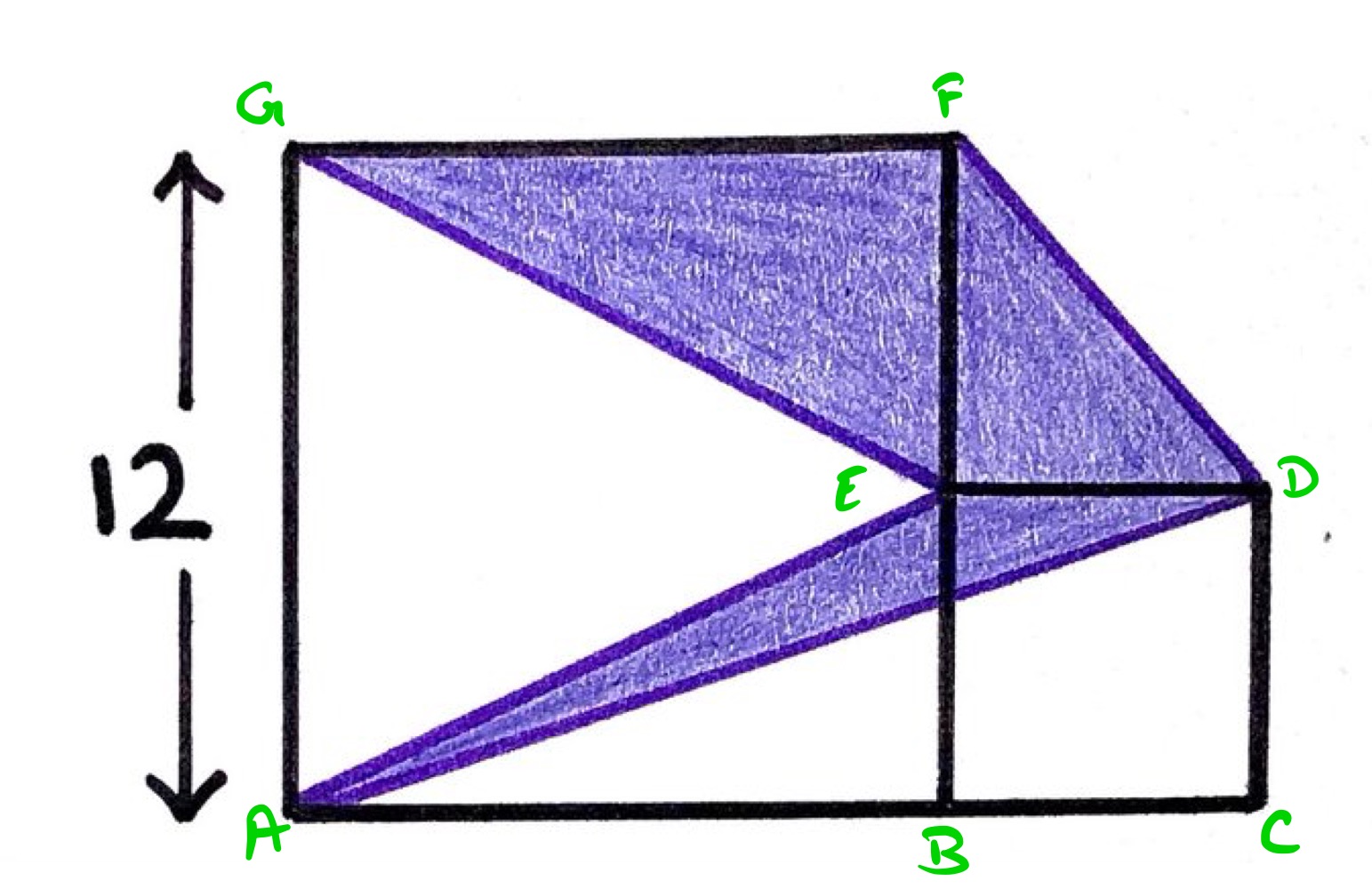
With the diagram labelled as above, let the side length of the smaller square be .
Then the area of triangle is .
Since has length , has length , so the area of trapezium is:
The total area is therefore:
Solution by Invariance Principle
The smaller square can vary in size leading to two configurations where the shaded area can be easily found.
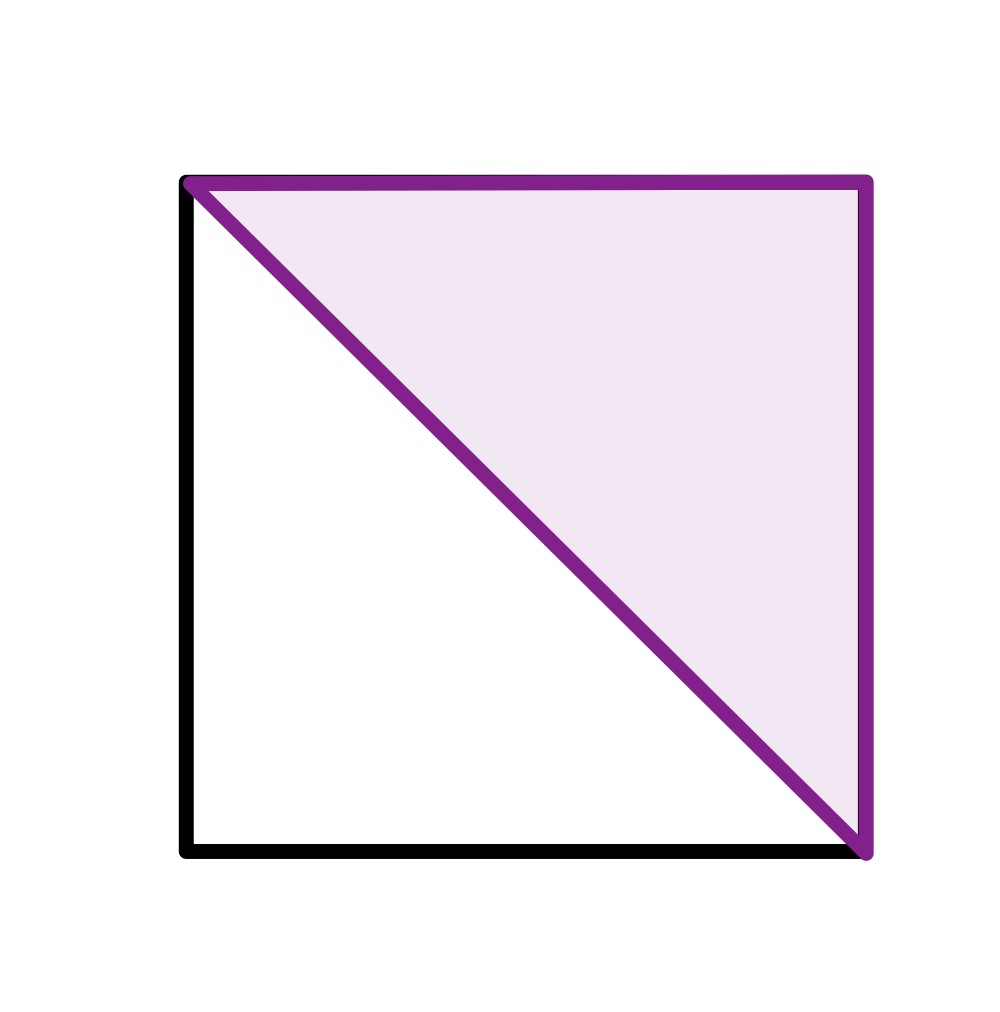
In this configuration, the smaller square has zero size meaning that the shaded area is half the remaining square, so has area .
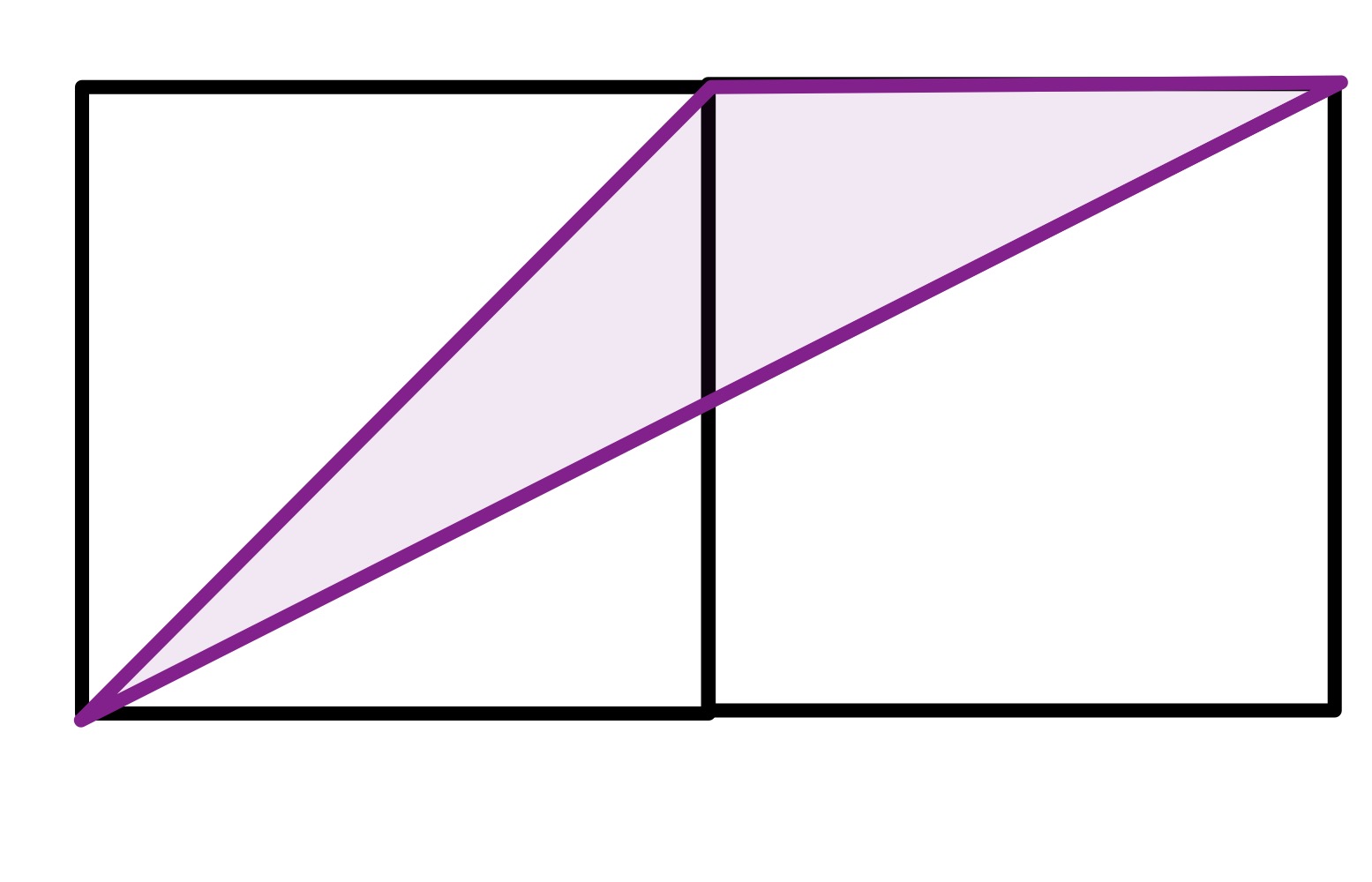
In this configuration both squares are the same size, meaning that the shaded area is a triangle with base and height meaning that its area is .