Notes
stacked hexagons solution
Stacked Hexagons
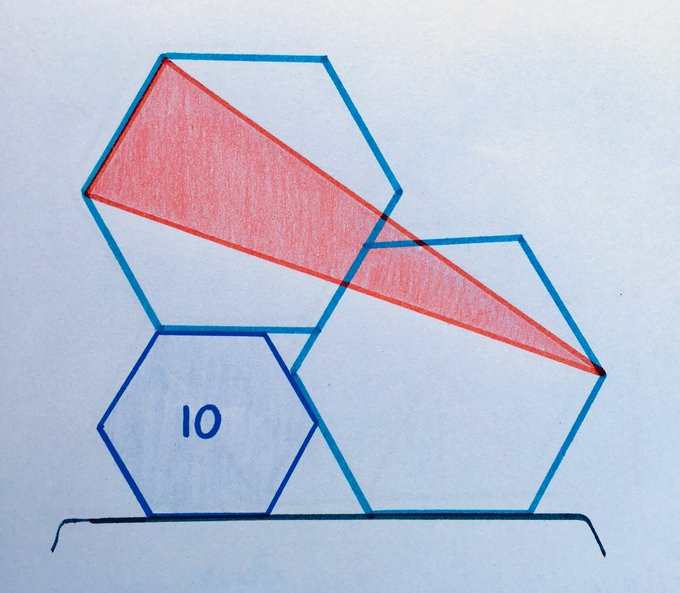
Two of the regular hexagons are identical; the third has an area . What’s the area of the red triangle?
Solution by Similarity, Area Scale Factor, and Properties of Hexagons
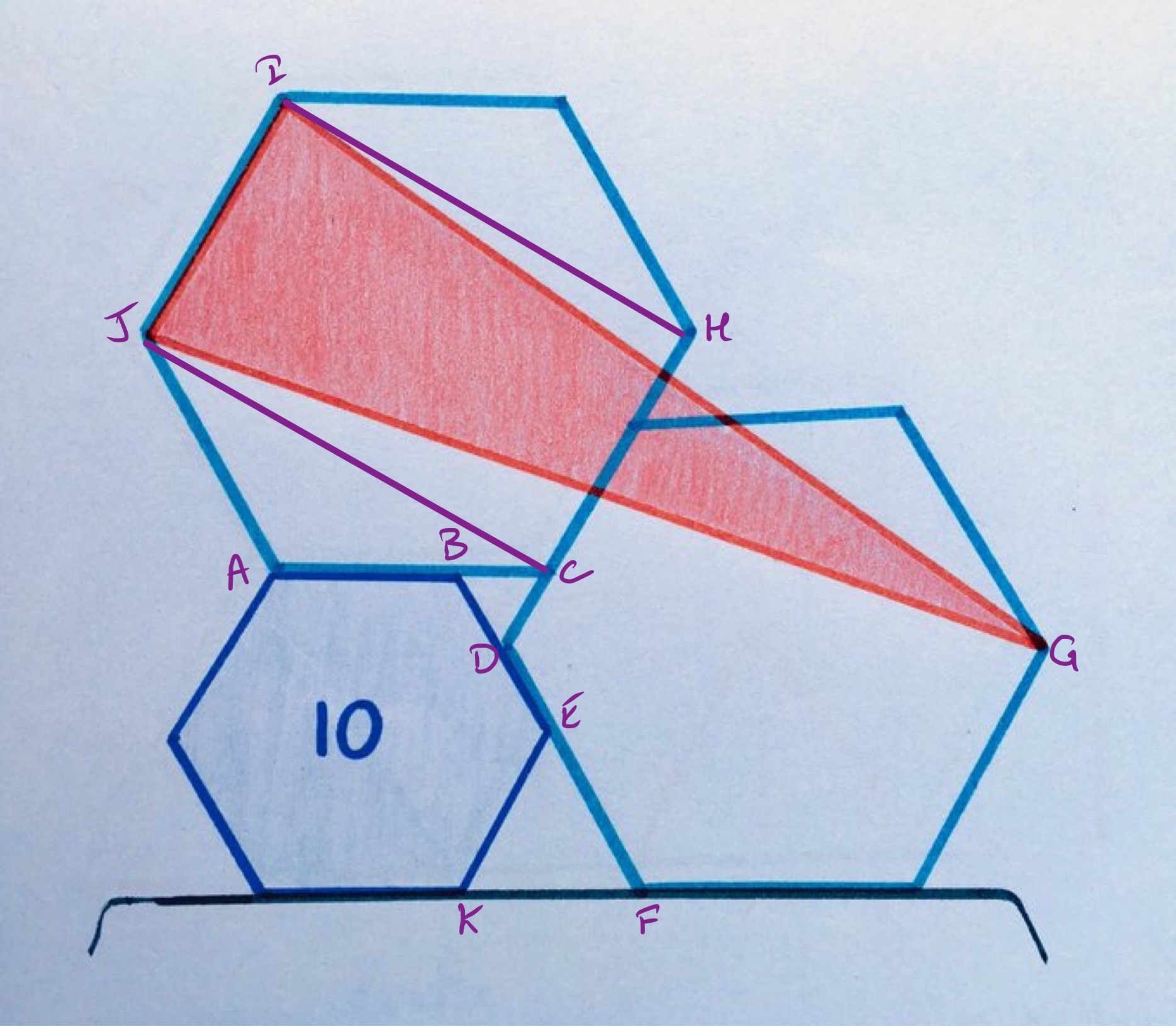
With the points labelled as above, let be the side length of the smaller hexagon and the side length of the larger hexagons. Triangle is equilateral, meaning that the combined length of and is the same as that of , so the length of to to is . Triangle is also equilateral, so the length of to to is the same as that of to to to , which is . So . The area scale factor from the smaller to larger is then so the larger hexagon has area .
The shaded triangle has base and its height above this base is twice the height of the hexagon. Its area is therefore the same as that of rectangle , which is two thirds of the area of the larger hexagon, so has area .