Notes
four squares iii solution
Solution to the Four Squares III Puzzle
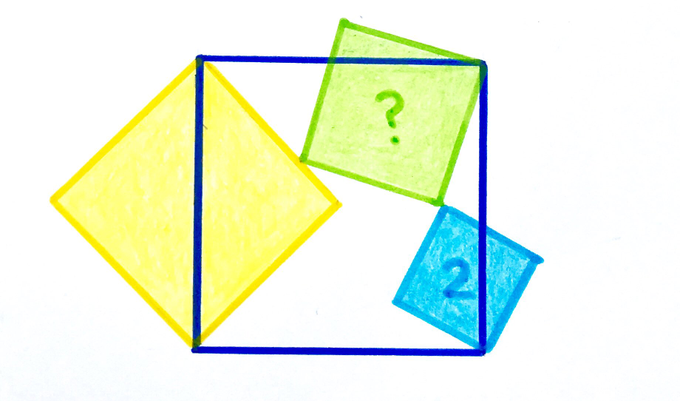
Four squares. The blue area is . What’s the green area?
Solution by Transformations
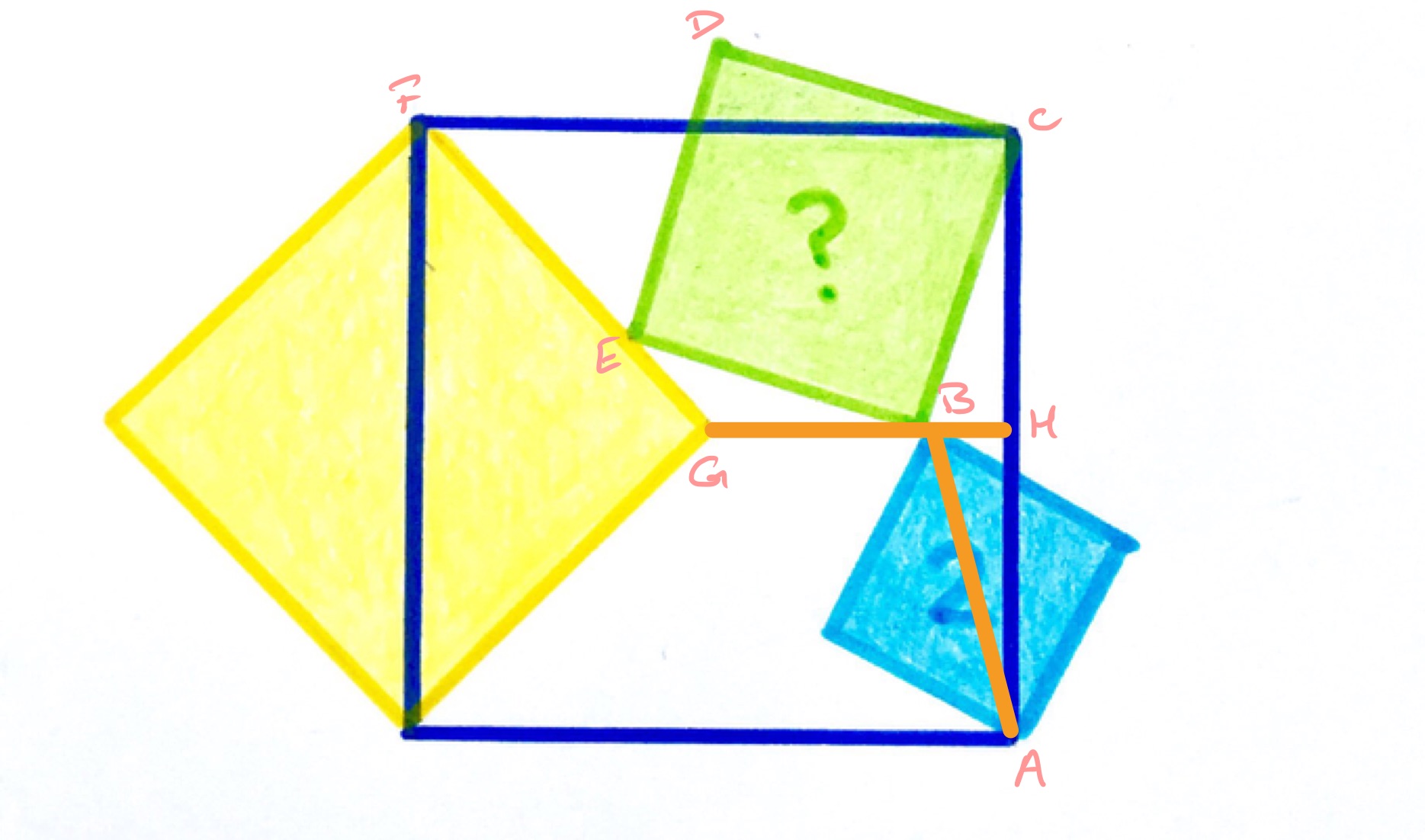
With the points labelled as in the above diagram, point moves along the line . With respect to the point , can be obtained from by a rotation by and a scaling by . As this is a fixed transformation, also moves along a straight line. When is at , is at , and when is at , is at . Hence moves along the line . As is the midpoint of the side , the lengths of and are equal. Since is the diagonal of the blue square and the side of the green square, the green square is twice the area of the blue square (this can be seen by dissecting each square into congruent isosceles right-angled triangles; the green into and the blue into ).
Hence the green square has area .
Solution by Invariance Principle
When the puzzle is in one of the two configurations where is at or where is at , the relationship between the green and blue squares is straightforward to see.